Do you know the correct resistance settings when building a new test program? While the default settings may work in most situations, you may find tests failing because of a wrong setting—not because of a bad cable. One of the most common settings in a situation like this is the resistance setting.
The resistance values are found in the low voltage settings of the test program. One setting is for connection or wire resistance while another sets insulation resistance. The tester will use these values to determine if the cable is good.
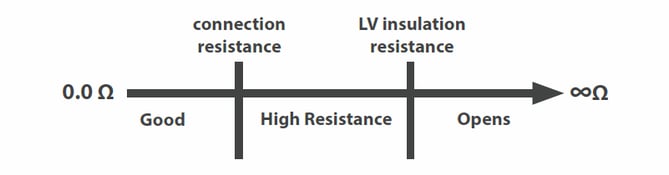
- Resistance detected below the connection resistance value means the tester found a connection between two test points. As long as the connection is intended, the cable will pass. (If the tester detects low resistance between two test points that are not intended to connect, it will report a short.)
- The tester ignores any resistance above the insulation resistance value. The insulation is creating a higher resistance barrier intended to separate the wires.
- Resistance detected between the connection resistance value and the insulation resistance value will create a high resistance error. This error will cause the test to fail.
All this is explained in the diagram below.
If your cables are constantly failing tests due to resistance errors, you may want to adjust the resistance settings. Cirris has tools and articles that explain how to do this.

Further Reading:
Resistance Is NOT Futile
Stop Spending So Much Time on Test Setup
3 Ways to Set Yourself Up for Wiring Errors