The information in this article comes from the Cirris Article, “AC Hipot Testing.”
Hipot testing involves using a high potential (voltage) to test insulation. A hipot test can be very useful in helping you develop a process that builds high quality cables and wire harnesses. There are two popular hipot voltage sources: DC and AC. This page introduces some of the concepts you'll find in AC hipot testing on the easy-wire CH2.
What is "AC Hipot?"
Hipot testing uses a high voltage source to make sure insulation is doing its job. An AC hipot test uses a voltage source that continually changes its voltage. The voltage alternates from positive to negative and back again. Generally there are 50 or 60 complete cycles of the alternating voltage each second.
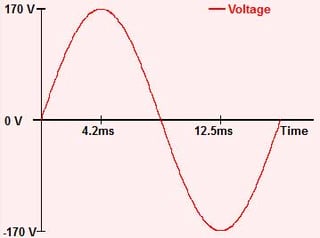
Hipot Testing Review
A hipot test starts with all of the points in a cable held at 0V. Then a single wire or network of connected points (called a net) is disconnected from 0V and connected to the AC source. The total current that flows is measured. If too much current is flowing the cable fails the hipot test.
Current
When the high voltage is applied, current will flow for several reasons. The two biggest reasons are insulation resistance and net-to-net capacitance.
The current flowing through the insulation resistance is proportional to the voltage. When the voltage is zero the resistive current is zero. When the voltage is at its peak, the resistive current is at its peak. This current is often called the "in-phase current", "resistive current", or "real current."
Read full article
Click the link below to read the full article on AC high voltage testing.

Further Reading:
What is the Difference between High Voltage and Hipot?
3 Reasons You Should Invest in High Voltage Testing
How to be Safe during High Voltage Testing